Die Funktion \(F\) ist eine Stammfunktion von \(f\). Geben Sie das Monotonieverhalten von \(F\) im Intervall \([1;3]\) an. Begründen Sie Ihre Angabe.
(2 BE)
Lösung zu Teilaufgabe 3b
\(F\) ist im Intervall \([1;3]\) streng monoton fallend.
Begründung
Stammfunktion
Eine differenzierbare Funktion \(F\) heißt eine Stammfunktion der Funktion \(f\), wenn für alle \(x \in D_f\) gilt:
\(F'(x) = f(x)\)
Für \(1 \leq x \leq 3\) verläuft der Graph von \(f\) unterhalb der \(x\)-Achse und es gilt \(F'(x) = f(x) < 0 \).
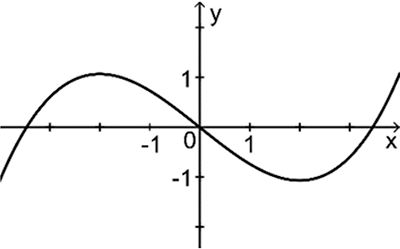 Abb. 2
Abb. 2Anwendung der Differetialrechnung:
Monotoniekriterium
\(\textcolor{#cc071e}{f'(x) < 0}\) im Intervall \( I \; \Rightarrow \; G_{f}\) fällt streng monoton in \(I\)
\(\textcolor{#0087c1}{f'(x) > 0}\) im Intervall \( I \; \Rightarrow \; G_{f}\) steigt streng monoton in \(I\)
(vgl. Merkhilfe)
Gemäß dem Monotoniekriteriem ist somit \(F\) im gegebenen Intervall streng monoton fallend.