Spiegelung eines Punktes an einer Ebene
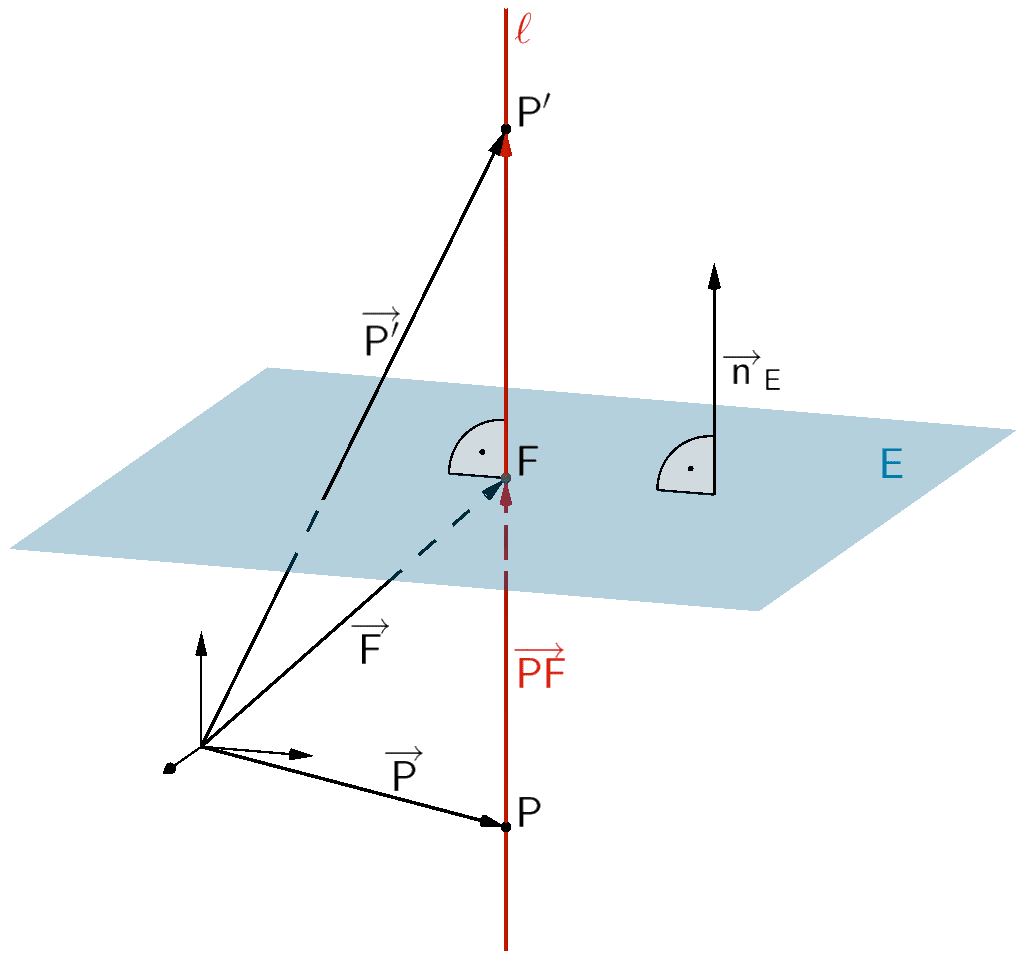
Es sei \(F\) der Lotfußpunkt des Lotes des Punktes \(P\) auf die Ebene \(E\). Die Entstehung des Bildpunktes \(P'\), der durch Spiegelung des Punktes \(P\) an der Ebene \(E \colon \overrightarrow{n}_{E} \circ (\overrightarrow{X} - \overrightarrow{A}) = 0\) hervorgeht. lässt sich auf die Spiegelung des Punktes \(P\) am Lotfußpunkt \(F\) zurückführen (vgl. Abiturskript - 2.6.1 Spiegelung eines Punktes an einem Punkt).
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{P} + 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{PF}\]
oder
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{F} + \overrightarrow{PF}\]
Man bestimmt den Verbindungsvektor \(PF\) bzw. den Lotfußpunkt \(F\), indem man die Lotgerade \(\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\) durch den Punkt \(P\) zur Ebene \(E\) aufstellt. Der Lotfußpunkt \(F\) ist der Schnittpunkt der Lotgerade \(\ell\) mit der Ebene \(E\) (vgl. Abiturskript - 2.3.4 Lotgeraden und orthogonale Ebenen, Lotgerade zu einer Ebene).
Der Verbindungsvektor \(\overrightarrow{PF}\) lässt sich in Abhängigkeit des Parameters \(\lambda\) der Gleichung der Lotgerade \(\ell\) beschreiben.
\[\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}\,; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\]
\[F \in \ell \colon \overrightarrow{F} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}\]
\[\overrightarrow{PF} = \overrightarrow{F} - \overrightarrow{P} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E} - \overrightarrow{P} = \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}\]
Schneidet man die Lotgerade \(\ell\) mit der Ebene \(E\), erhält man genau den Wert des Parameters \(\lambda\), der den Verbindungsvektor \(\overrightarrow{PF}\) festlegt (vgl. Abiturskript - 2.3.2 Lagebeziehung von Gerade und Ebene, Bestimmung des Schnittpunkts).
\[E \colon \overrightarrow{n}_{E} \circ (\overrightarrow{X} - \overrightarrow{A}) = 0\]
\[\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}\,; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\]
\[\ell \cap E \colon \overrightarrow{n}_{E} \circ (\overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E} - \overrightarrow{A}) = 0\]
\(\Longrightarrow \quad\)Parameterwert für \(\lambda\)
\(\Longrightarrow \quad\)Verbindungsvektor \(\overrightarrow{PF}\) und \(F \in \ell\)
Beispielaufgabe
Gegeben sei die Ebene \(E \colon x_{1} +2x_{2} + 4x_{3} - 20 = 0\) und der Punkt \(P(3|5|7)\).
Bestimmen Sie die Koordinaten des Punktes \(P'\), der durch Spiegelung des Punktes \(P\) an der Ebene \(E\) hervorgeht.
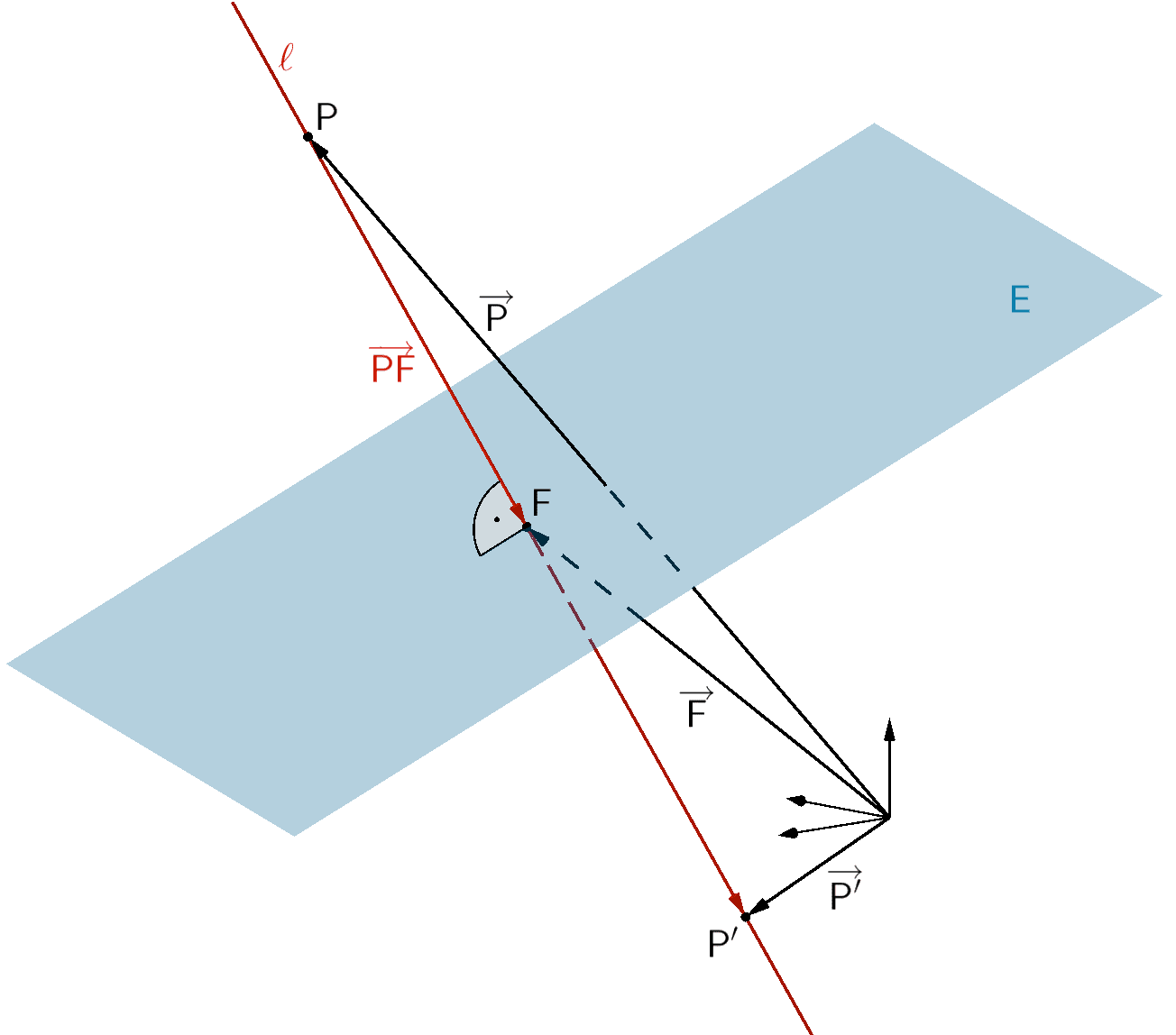
Es sei \(F\) der Lotfußpunkt des Lotes des Punktes \(P\) auf die Ebene \(E\)
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{P} + 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{PF}\]
oder
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{F} + \overrightarrow{PF}\]
Gleichung der Lotgerade \(\ell\) formulieren (vgl. Abiturskript - 2.3.4 Lotgeraden und orthogonale Ebenen, Lotgerade zu einer Ebene):
\[P(3|5|7)\]
\[E \colon x_{1} +2x_{2} + 4x_{3} - 20 = 0 \quad \Longrightarrow \quad \overrightarrow{n}_{E} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}\]
\[\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \overrightarrow{P} + \lambda \cdot \overrightarrow{n}_{E}; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\]
\[\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} + \lambda \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\]
Verbindungsvektor \(PF\) in Abhängigkeit des Parameters \(\lambda\) der Gleichung der Lotgerade \(\ell\) beschreiben:
\[P(3|5|7)\]
\[F \in \ell \colon \overrightarrow{F} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} + \lambda \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 + \lambda \\ 5 + 2\lambda \\ 7 + 4\lambda \end{pmatrix}\]
\[\overrightarrow{PF} = \overrightarrow{F} - \overrightarrow{P} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 + \lambda \\ 5 + 2\lambda \\ 7 + 4\lambda \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} \lambda \\ 2\lambda \\ 4\lambda \end{pmatrix} = \lambda \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}\]
Lotgerade \(\ell\) mit der Ebene \(E\) schneiden (vgl. Abiturskript - 2.3.2 Lagebeziehung von Gerade und Ebene, Bestimmung des Schnittpunkts):
\[\ell \colon \overrightarrow{X} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} + \lambda \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix}; \; \lambda \in \mathbb R\]
\[E \colon x_{1} +2x_{2} + 4x_{3} - 20 = 0\]
\[\begin{align*} \ell \cap E \colon 3 + \lambda + 2 \cdot (5 + 2\lambda) + 4 \cdot (7 + 4\lambda) - 20 &= 0 \\[0.8em] 3 + \lambda + 10 + 4\lambda + 28 + 16\lambda - 20 &= 0 \\[0.8em] 21\lambda + 21 &= 0 & &| - 21 \\[0.8em] 21\lambda &= -21 & &| : 21 \\[0.8em] \lambda &= -1 \end{align*}\]
Verbindungsvektor \(PF\) und ggf. Ortsvektor \(\overrightarrow{F}\) berechnen:
\[\overrightarrow{PF} = \lambda \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} = (-1) \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ -2 \\ -4 \end{pmatrix}\]
\[F \in \ell \colon \overrightarrow{F} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} + (-1) \cdot \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix}\]
Koordinaten des Punktes \(P'\) berechnen:
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{P} + 2 \cdot \overrightarrow{PF} = \begin{pmatrix} 3 \\ 5 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix} + 2 \cdot \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ -2 \\ -4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ -1 \end{pmatrix}\]
oder
\[\overrightarrow{P'} = \overrightarrow{F} + \overrightarrow{PF} = \begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 3 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} -1 \\ -2 \\ -4 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ -1 \end{pmatrix}\]
\[\Longrightarrow \quad P'(1|1|-1)\]