Gegeben ist die Funktion \(g \colon x \mapsto (x^{2} - 9x) \cdot \sqrt{2 - x}\) mit maximaler Definitionsmenge \(D_{g}\). Geben Sie \(D_{g}\) und alle Nullstellen von \(g\) an.
(3 BE)
Lösung zu Teilaufgabe 2a
\[g(x) = (x^{2} - 9x) \cdot \sqrt{2 - x}\]
Maximale Definitionsmenge \(D_{g}\)
Maximale Definitionsmenge bestimmen
Gebrochenrationale Funktion / Quotient von Funktionen
\[x \mapsto \dfrac{Zähler(x)}{\textcolor{#e9b509}{\underbrace{Nenner(x)}_{\Large{\neq \, 0}}}}\]
Nullstelle(n) des Nenners ausschließen!
Wurzelfunktion
\[x \mapsto \sqrt{\mathstrut\smash{\textcolor{#e9b509}{\underbrace{\dots}_{\Large{\geq\,0}}}}} \\ {}\]
Der Wert des Terms unter der Wurzel (Radikand ) darf nicht negativ sein!
(natürliche) Logarithmusfunktion
\(x \mapsto \ln{(\,\textcolor{#e9b509}{\underbrace{\dots}_{\Large{>\,0}}}\,)}\) bzw. \(x \mapsto \log_{a}{(\,\textcolor{#e9b509}{\underbrace{\dots}_{\Large{>\,0}}}\,)}\)
Die (Natürliche) Logarithmusfunktion ist in \(\textcolor{#e9b509}{\mathbb R^{+}}\) definiert!
Der Wurzelterm \(\sqrt{2 - x}\) schränkt die Definitionsmenge der Funktion \(g\) ein. Der Radikand (Ausdruck unter der Wurzel) \(\textcolor{#cc071e}{2 - x}\) darf nicht negativ sein.
\[\textcolor{#cc071e}{2 - x \geq 0} \enspace \Leftrightarrow \enspace x \leq 2 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace D_{g} = \; ]-\infty;2]\]
Nullstellen von \(g\)
Satz vom Nullprodukt: Ein Produkt ist genau dann gleich Null, wenn einer der Faktoren Null ist.
Nullstelle(n) einer Funktion bestimmen
Eine Nullstelle ist die \(x\)-Koordinate eines gemeinsamen Punktes des Graphen einer Funktion \(x \mapsto f(x)\) mit der \(x\)-Achse. An einer Nullstelle gilt: \(f(x) = 0\).

Satz vom Nullprodukt: Ein Produkt ist genau dann null, wenn einer der Faktoren null ist.
\(f(x) \cdot g(x) = 0 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace f(x) = 0\) oder \(g(x) = 0\)
Ein Quotient von Funktionen ist genau dann null, wenn die Zählerfunktion null ist.
\(\dfrac{f(x)}{g(x)} = 0 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace f(x) = 0\; (g(x) \neq 0)\)
Lösungsformel für quadratische Gleichungen (Mitternachtsformel, vgl. Merkhilfe)
\[\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}x^2 + \textcolor{#0087c1}{b}x + \textcolor{#e9b509}{c} = 0 \enspace \Leftrightarrow \enspace x_{1,2} = \frac{-\textcolor{#0087c1}{b} \pm \sqrt{\textcolor{#0087c1}{b}^2 - 4\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}\textcolor{#e9b509}{c}}}{2\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}\]
Diskriminante \(D = b^2 -4ac \;\):
\(D < 0\,\): keine Lösung
\(D = 0\,\): genau eine Lösung
\(D > 0\,\): zwei verschiedene Lösungen
Folgende Fälle lassen sich einfacher durch Umformung lösen:
\[\begin{align*}\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}x^2 + \textcolor{#0087c1}{b}x &= 0 &&| \; x\; \text{ausklammern (Produkt formulieren)} \\[0.8em] x \cdot (ax + b) &= 0 \\[0.8em] \Rightarrow \enspace x = 0 \vee ax + b &= 0 \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*}\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}x^2 + \textcolor{#e9b509}{c} &= 0 &&| -c \enspace (c \neq 0) \\[0.8em] ax^2 &= -c &&| : a \\[0.8em] x^2 &= -\frac{c}{a} &&| \; \sqrt{\quad} \\[0.8em] x_{1,2} &= \pm \sqrt{-\frac{c}{a}} \end{align*}\]
Zwei Lösungen, falls \(-\dfrac{c}{a} > 0\), keine Lösung, falls \(-\dfrac{c}{a} < 0\)
Vorgehensweise für die Bestimmung der Nullstelle(n) einer ganzrationalen Funktion ab Grad 3:
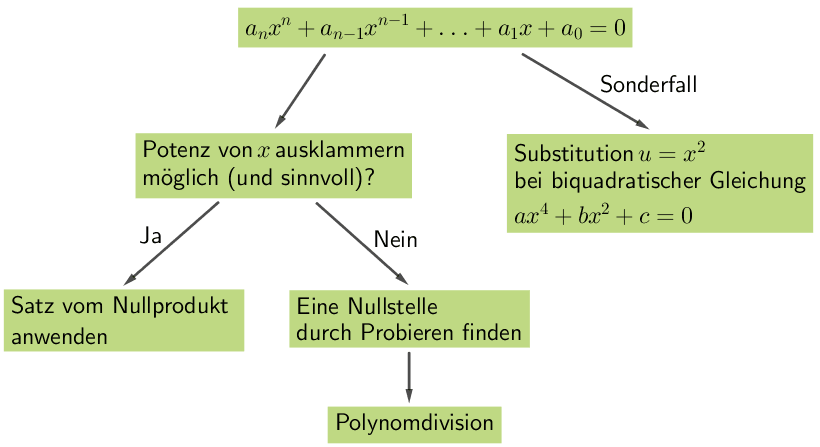
vgl. Abiturskript - 1.1.3 Ganzrationale Funktion, Nullstellen
Nullstellen einer gebrochenrationalen Funktion \(f(x) = \dfrac{\textcolor{#0087c1}{z(x)}}{n(x)}\) sind alle Nullstellen des Zählerpolynoms \(\textcolor{#0087c1}{z(x)}\), die nicht zugleich Nullstellen des Nennerpolynoms \(\boldsymbol{n(x)}\) sind.
Ist \(x_0\) eine Nullstelle des Zählerpolynoms \(\boldsymbol{z(x)}\) und zugleich eine vollständig kürzbare Nullstelle des Nennerpolynoms \(\boldsymbol{n(x)}\), so besitzt die gebrochenrationale Funktion \(f\) an der Stelle \(x_0\) eine hebbare Definitionslücke.
(vgl. Abiturskript - 1.2.1 Gebrochenrationale Funktion, Nullstellen und Polstellen)
Eine Wurzelfunktion \(f(x) = \sqrt{\textcolor{#cc071e}{g(x)}}\) nimmt genau dann den Wert null an, wenn der Radikand (Term unter der Wurzel) null ist.
\[\sin{x} = 0 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace x = k \cdot \pi \; (k \in \mathbb Z)\]
\[\cos{x} = 0 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace x = \dfrac{\pi}{2} + k \cdot \pi \; (k \in \mathbb Z)\]
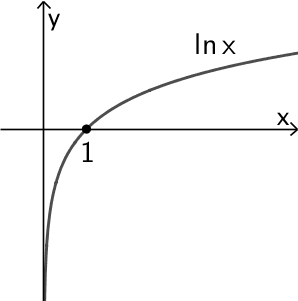
Die natürliche Logarithmusfunktion \(x \mapsto \ln{x}\) besitzt die einzige Nullstelle \(\boldsymbol{x = 1}\).
\[\ln{\left( \textcolor{#0087c1}{f(x)} \right)} = 0 \enspace \Rightarrow \enspace \textcolor{#0087c1}{f(x) = 1}\]
Die natürliche Exponentialfunktion \(x \mapsto e^x\) sowie jede verkettete Funktion \(x \mapsto e^{f(x)}\) besitzt keine Nullstelle!
\[g(x) = \textcolor{#0087c1}{(x^{2} - 9x)} \cdot \textcolor{#e9b509}{\sqrt{2 - x}}; \; D_{g} = \; ]-\infty;2]\]
\[\begin{align*} \textcolor{#0087c1}{(x^{2} - 9x)} &= 0 \\[0.8em] x \cdot (x - 9) &= 0 &&| \; D_{g} = \; ]-\infty;2] \\[0.8em] \Rightarrow \enspace x_{1} &= 0 \\[0.8em] (x &= 9 \textcolor{#cc071e}{\notin} D_{g}) \end{align*}\]
\[\begin{align*}\textcolor{#e9b509}{\sqrt{2 - x}} &= 0 \\[0.8em] \Rightarrow \enspace x_{2} &= 2\end{align*}\]